1.6 KiB
Executable File
1.6 KiB
Executable File
| author | date | title | tags | uuid | lecture_slides | exercise_sheets | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akbar Rahman | \today | MMME2051 // AC Power |
|
c269b4b7-7835-4b50-8d4f-ff5bc63a8a3d |
|
|
This section builds on introduction to AC.
Definitions
- Phase voltage - voltage across any phase
- Line voltage - voltage between two live lines
- Phase current - current through any phase
- Line current - current through any live line
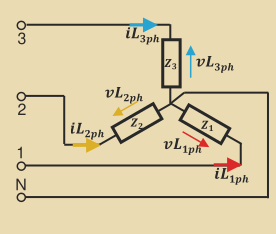
Three-Phase Load
P = \sqrt{3} V_lI_l\cos\gamma-
3-phase devices (source and load) are usually balanced, meaning that the impedance in each phase is equal (
Z_1 = Z_2 = Z_3). -
For loads, this means that the voltage across them are the same, apart from the phase angles:
\begin{align*} v_{1N} = V\cos{2\pi ft} \ v_{2N} = V\cos{2\pi ft - \frac{2\pi}{3}} \ v_{3N} = V\cos{2\pi ft + \frac{2\pi}{3}} \end{align*}
-
Balanced loads and sources ensure that line/phase currents have equal magnitudes and that the neutral current is 0
Star Load
|V_\text{line}| = \sqrt 3 |V_\text{phase}|I_\text{line} = I_\text{phase}Delta Load
|V_\text{line}| = |V_\text{phase}|I_\text{line} = \sqrt 3 I_\text{phase}Power Factor (PF)
\text{PF} = \cos{\gamma} = \cos{\left(\Phi_v-\Phi_i\right)}